Detection, prevention and response to cyber threats
SIEM and EDR
The functions
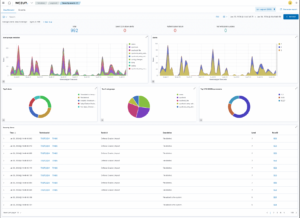
- Intrusion Detection (IDS/IPS)
- Correlation of Events
- Analysis of logs
- Vulnerability Management
- Compliance and reporting
- Extensibility and integrations
- Correlation and « Threat Intelligence »
Areas of application
- Intrusion Detection
- Checking the integrity of files
- Vulnerability detection / configuration assessment
- Regulatory Compliance
- Reporting
Some examples of use cases
- Checking the integrity of files
- Verifying compliance of configuration files (tampering by a third-party program)
- Checking the proper functioning of the antivirus on the workstations
- Ransomware Detection
- MAC address flapping detection on network equipment
- DDOS attack detection
- Alert for massive authentication error (Web, 802.1X …)
Principle of operation
- A manager centralizing events
- Agents on each workstation or server, registered with the manager
- The manager defines the monitoring rules (e.g. number of failed login attempts)
- Agents apply actions if a rule matches (e.g. block IP)
- Agents report events to the manager
- The manager can take additional actions (e.g. isolate the machine from the network)
Architecture
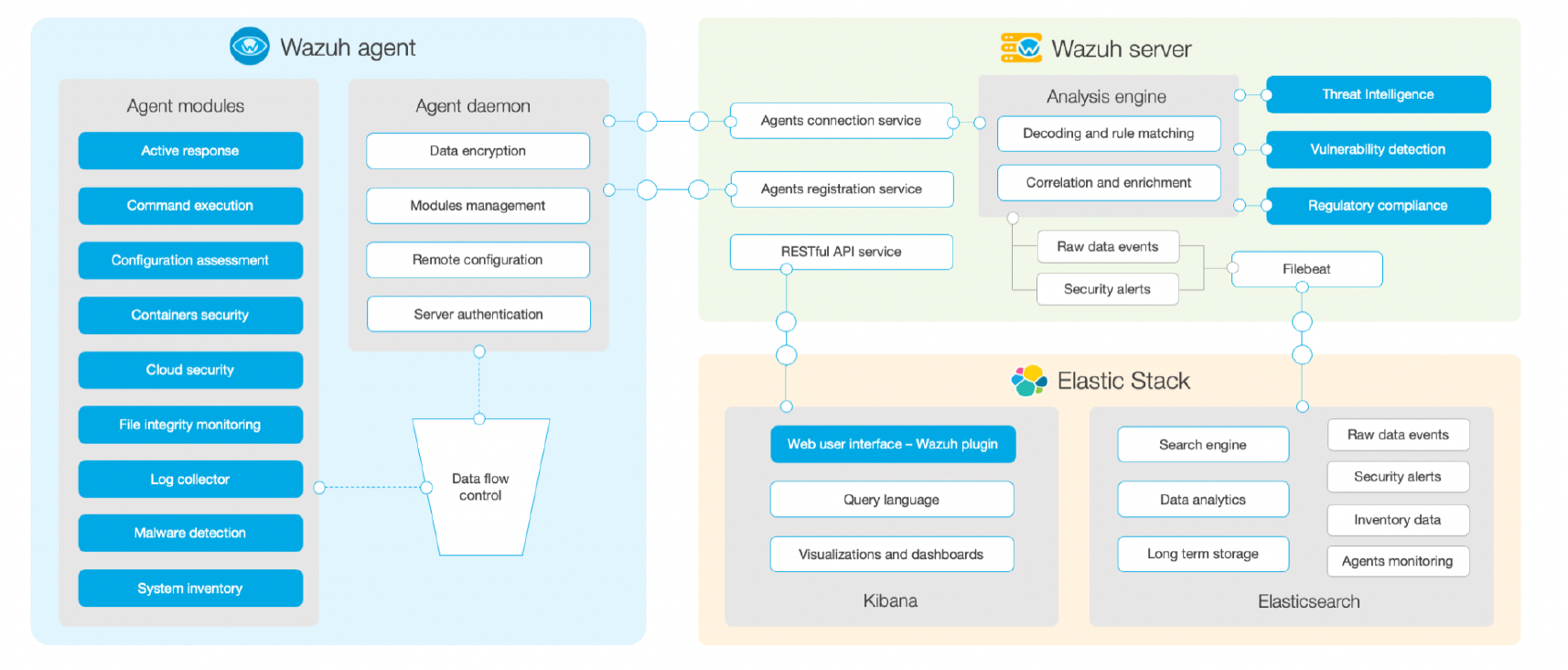
Components
Agent
Installed on the end devices, it sends information back to the server
Server
Analyzes and indexes alerts generated by the server
Interface
Allows visualization of data
Indexer
Stores and indexes server-generated alerts


